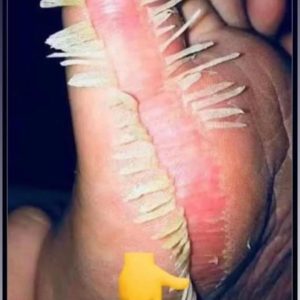
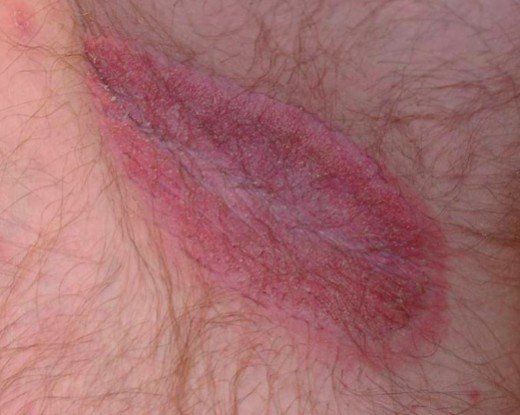
Armpit yeast infections, also known as candidiasis or intertrigo, occur when the yeast Candida grows excessively in the warm and moist areas of the skin, such as the armpits. Candida is a type of fungus that is normally present on the skin in small amounts, but factors such as warm and humid conditions, poor hygiene, compromised immune system, or certain medications can contribute to its overgrowth.
Common symptoms of an armpit yeast infection include:
- Redness and inflammation
- Itching or a burning sensation
- Rash or patches of red, moist skin
- Odor
- Small, raised bumps or pustules
Here are some general tips for managing and preventing armpit yeast infections:
- Keep the area clean and dry: Wash the affected area regularly with mild soap and water. Pat the skin dry thoroughly after bathing.
- Avoid tight clothing: Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing to minimize friction and allow air circulation.
- Use antifungal creams or powders: Over-the-counter antifungal creams or powders containing ingredients like clotrimazole or miconazole can help treat the infection. Follow the product’s instructions.
- Practice good hygiene: Shower regularly, and pay extra attention to cleaning and drying the armpit area. Avoid using harsh soaps or irritating substances.
- Keep the area cool: Try to stay in a cool and dry environment. Avoid excessive sweating, and consider using talcum powder or cornstarch to help absorb moisture.
- Change wet or damp clothing promptly: If your clothing becomes wet, change into dry clothes as soon as possible.
- Consider your diet: Some people find that reducing their intake of sugar and refined carbohydrates can help prevent yeast overgrowth. A balanced and healthy diet can contribute to overall immune system health.
If the symptoms persist or worsen despite these measures, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment. They may prescribe stronger antifungal medications or recommend other interventions based on the specific circumstances of the infection.